Euphorbiaceae
Martretia quadricornis
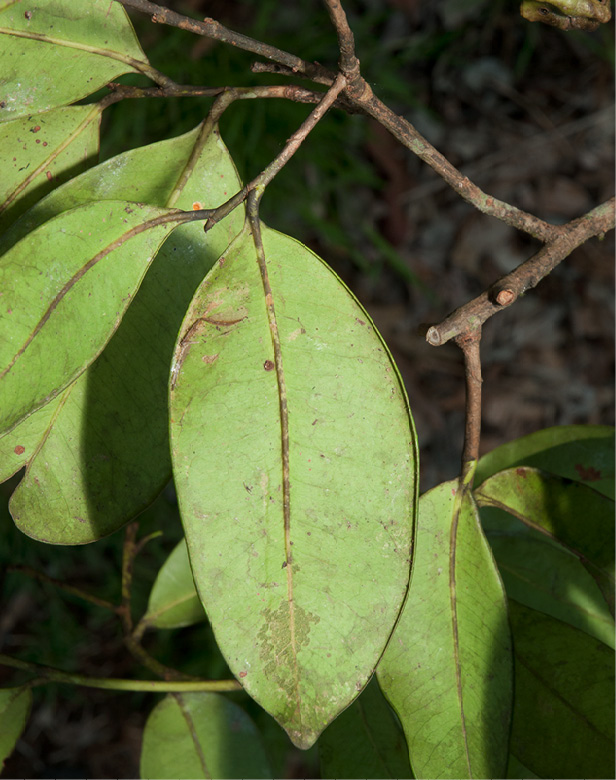
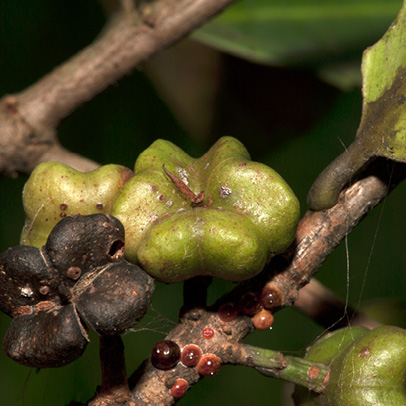
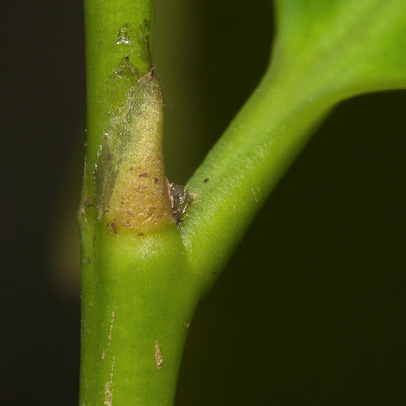







- Mature leaf, lower surface.
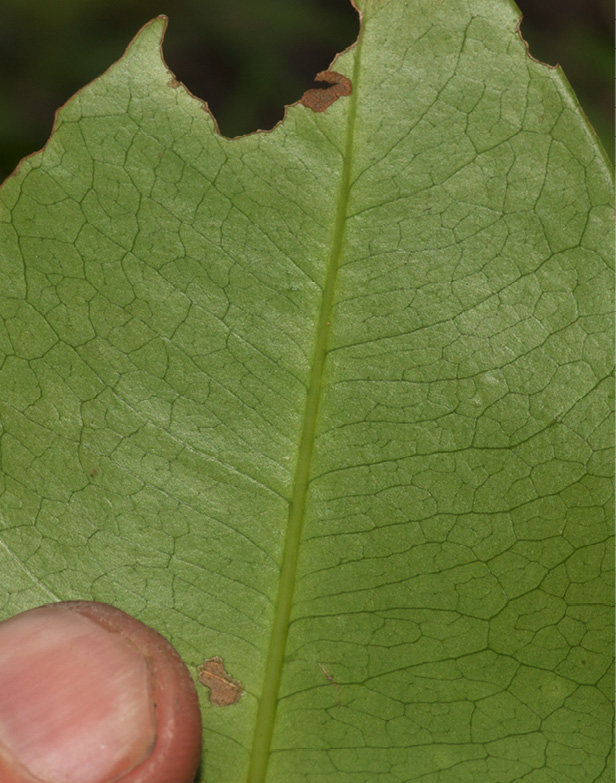
- Midrib and venation, lower surface.
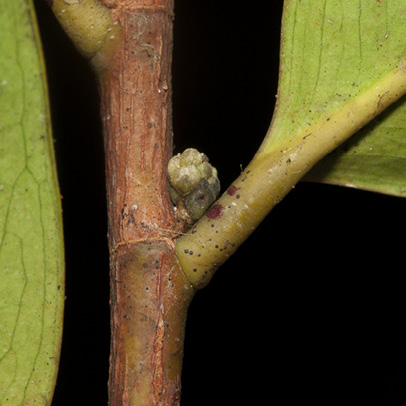
- Petiole, bud and stipular scar.
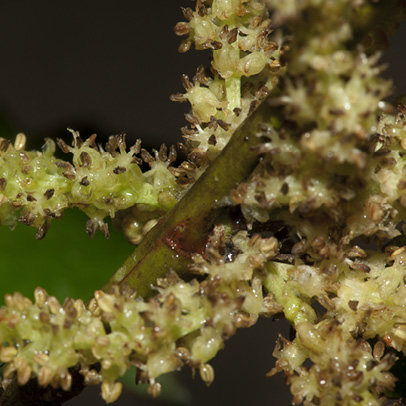
- Inflorescence.
- Fruit.
- Petiole with stipule before falling.
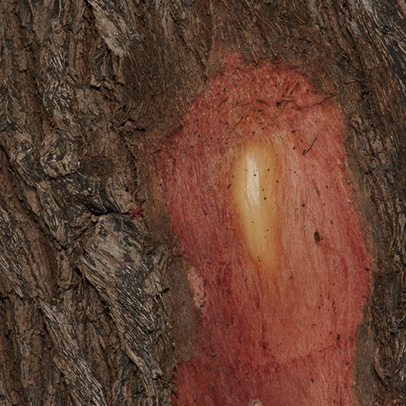
- Bark.
- Slash.
General Information
This species has few distinguishing features from a distance. Up close, however, the paired stipules at the base of the petiole leave a distinct scar when they fall. These two scars almost meet on the other side of the twig to form a ring but there is a slight gap. The scars could, at first glance, look like those of Ficus or Irvingiaceae. The next thing to notice is the lack of clearly defined secondary veins which are rather close in prominence to the tertiary venation. This gives the impression of a broadly reticulate network of venation. The secondary veins do loop some distance from the leaf margin which is inrolled below. These characters, together with the rather leathery leaves, make this species easy to identify the second time you see it. The fruit are the most distinct feature. They are wider than they are long and are usually four-lobed with the remains of the double style.
Ecology
The trees are either male or female and always grow by water.
Distribution
Distribution: Sierra Leone to DRC and Gabon.
